Edge Computing with KubeEdge
Cloud computing is far away from terminal devices (such as cameras, sensors, etc.). For real-time computing requirements, placing calculations on the cloud can cause long network delays, network congestion, and degradation of service quality. Terminal devices usually have insufficient computing power and cannot be compared to the cloud. In this case, edge computing came into being, extending the cloud computing power to the edge nodes close to the terminal device, which perfectly solved the above problem.
As the world's first open source edge computing platform for Kubernetes, KubeEdge relies on Kubernetes' container orchestration and scheduling capabilities to provide the ability to extend the application on the cloud to the edge by managing the edge nodes of the user, and to link the data on the edge side and the cloud to meet the requirements. Customer's remote control, data processing, analysis and decision-making, and intelligent appeal for edge computing resources. At the same time, it provides unified equipment/application monitoring, log collection and other operation and maintenance capabilities in the cloud, providing enterprises with complete edge computing solutions for integrated cloud and cloud services.
Device Health and KubeEdge Device Management
Speaking of IoT devices, one has to mention a concept called Device Twin. As a virtual mapping of IoT device metadata on the application platform, device twinning has become an important part of IoT device management. IoT devices usually contain two types of data: one is metadata that will not be changed, including the serial number, asset identifier, Mac address, etc., and the detailed information describing the device. It can also be called the static attribute of the device. The other type is the dynamic data of the device, including device-specific real-time data in a specific context, such as the on and off state of the lamp, which can also be called the Twin property of the device. Device twins have the same characteristics as physical devices, allowing for better communication between devices and applications. The command sent by the application first arrives at the device, and the device updates the status according to the Expected State set by the application. In addition, the IoT device feeds back its own Actual State in real time, and the device detects both the Actual State and the Expected State of the IoT device. This approach also allows the state of the device to be synchronized when the IoT device goes online again offline.
Device management is also a key feature of IoT scenarios in edge computing. KubeEdge is an open-source edge computing platform with both cloud and edge. In addition to implementing cloud application configuration and delivery, another important function is to manage IoT devices in the cloud and synchronize device state between cloud edges.
KubeEdge Device Management Component
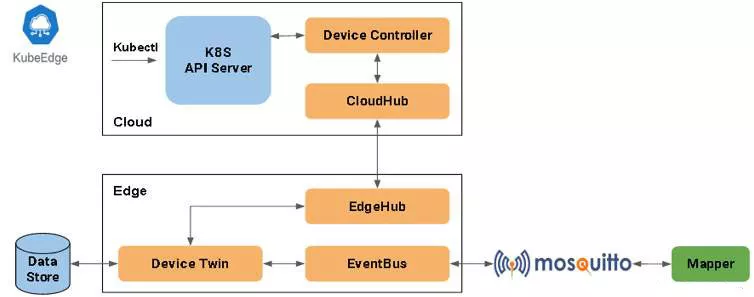
The components related to KubeEdge device management are as follows:
DeviceController: An extended Kubernetes controller that manages device information in the cloud and synchronizes the cloud with edge devices.
CloudHub: The WebSocket server is responsible for monitoring cloud resource changes, caching and sending messages to EdgeHub.
EdgeHub: WebSocket client, including the ability to synchronize cloud resource updates, report edge nodes, and device information to the cloud.
DeviceTwin: Responsible for storing device status and synchronizing device status to the cloud.
EventBus: A client that interacts with the MQTT server Mosquitto to provide subscription and publish messages for other components.
Mapper: Used to connect and control end-side devices, such as turning lights on and off.
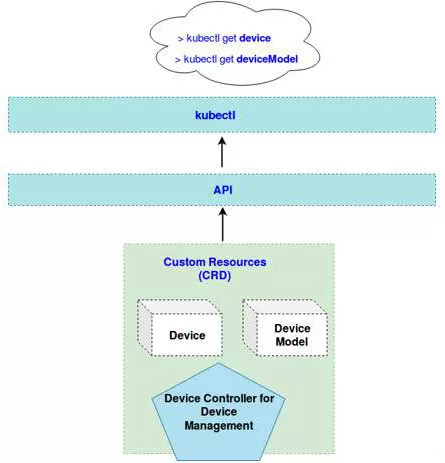
KubeEdge extends Kubernetes' API through CRD (Customer Resource Definition). The extended API resources include: Device and DeviceModel, so that we can perform CRUD operations on device resources in the cloud through Kubernetes command line tool Kubectl or other means. The Device resource maps devices associated with each edge node, such as sensors. DeviceModel is a template defined for a class of devices. It is convenient for users to perform batch operations on Device resources easily in the cloud based on the DeviceModel template.
Light up your home with KubeEdge
Light up your home in the clouds, let's see how KubeEdge does this interesting thing? A reference example of a device generation is as follows:

Here you need to use the above mentioned Device Twin. For example, the metadata information of the lamp is described above in Json format, including static attribute attributes and dynamic attribute twin. This defines a twin property called powerstatus, whose expected and actual values can be either ON or OFF. The device itself can report the actual value of the powerstatus to the cloud. The cloud can control the edge side lights to be turned on and off by changing to the expected value of the powerstatus attribute.
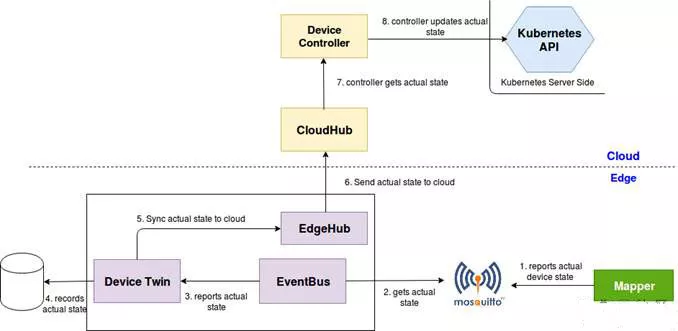
First we look at how to report the actual value of the powerstatus to the cloud:
The Mapper reports the actual status of the Actual State to the MQTT server Mosquitto in real time.
The EventBus receives a subscription message from Mosquitto, which contains the actual state of the device, Actual State.
EventBus sends the actual state of the device to Device Twin.
Device Twin updates the device's actual state to a lightweight database local to the edge node, such as SQLite.
Device Twin synchronizes the actual state to the WebSocket client EdgeHub.
EdgeHub sends a message to the WebSocket server CloudHub.
CloudHub returns a message to DeviceController.
DeviceController synchronizes the actual state of the Actual State to the Kubernetes API Server.
Finally, the user can query the actual value of the powerstatus of the device in the cloud to obtain the actual state of the light on and off on the edge device.
Join KubeEdge
Device management is undoubtedly a key feature in the edge computing IoT scenario. Currently, KubeEdge's device management features are still under development and will be released in version 0.3, so stay tuned.
As a 100% open source project, KubeEdge welcomes you. KubeEdge Github project address: Https://github.com/kubeedge/kubeedge
Instructions on how to setup KubeEdge can be found here